Concerns over the safety of lens care products, along with continuing interest in dry eye, potential risks associated with lens wear and handling, maximizing visual quality and the impact of the environment all contributed to studies being presented at this year's meeting. (Unless otherwise specified, studies summarized below had no commercial support.)
Dry Eye Concerns
A study conducted in the United Kingdom compared tear-film evaporation rates in 107 soft contact lens wearers and 166 non-contact-lens wearers to determine whether higher rates of evaporation accompanied use of a contact lens—even in the absence of symptoms. Participants were age-matched; tear-film evaporation was measured with the Oregon Health Sciences University Evaporimeter; symptoms were quantified using the McMonnies questionnaires.
Key findings included:
• The incidence of dry eye was higher for contact lens wearers than for non-wearers (46 percent vs. 23 percent, p<0.05). (Not surprisingly, in both groups, those with symptoms showed higher evaporation rates than those without symptoms.)
• Among subjects with symptoms, the evaporation rate was significantly higher for CL wearers than for non-wearers, whether the humidity was 30 or 40 percent (p<0.05).
• Among subjects without symptoms, the rate of evaporation was also significantly higher for CL wearers than for non-wearers at both humidity levels (p<0.05).
The researchers conclude that a soft contact lens in the eye is a contributing factor in producing a higher rate of tear-film evaporation, whether or not symptoms are present.5412
In a study conducted by researchers in
Findings include:
• Cumulative dehydration was relatively uniform for the first five minutes—about 1.5 percent/minute. After that, higher levels of water content tended to display greater cumulative dehydration.
• HEMA-based hydrogels dehydrate more, and faster, than silicone-hydrogel materials.
• No significant differences were found between conventional hydrogels and those that claimed to reduce on-eye dehydration.5368
A study conducted by a group of researchers affiliated with CIBA Vision attempted to determine how the level of dry-eye symptoms that remains after switching from hydrogel lenses to lotrafilcon A or B silicone hydrogel lenses compared to levels of dry eye found in non-contact-lens-wearing subjects.
They first compared the prevalence of "frequent" or "constant" dryness reported by age-matched groups of 259 contact lens wearers and 246 non-wearers in a historical, cross-sectional sampling of dry-eye questionnaires. (See graph, below.) Non-wearers were 47 percent less likely to report frequent or constant dryness than contact lens wearers (p=0.0001).
Next, they calculated the longitudinal change in dryness frequency found in four prospective studies in which a total of 1,036 daily wear hydrogel lens wearers were refitted with silicone hydrogel lenses for daily or continuous wear. In these four trials:
• Subjects refitted with daily wear lotrafilcon A lenses showed a drop of 67 percent in reports of frequent or everyday dryness during the day, and a drop of 62 percent in these reports at the end of the day (both p<0.0001).
• Subjects refitted with lotrafilcon A lenses designed for continuous use for up to 30 nights and days showed a drop of 63 percent in these reports during the day and a drop of 41 percent at the end of the day (p=0.014 and p=0.02, respectively).
• Subjects refitted with lotrafilcon B lenses for daily wear showed a 48 percent drop in these reports during the day, and a 46 percent reduction at the end of the day (both p<0.0001).
• Overall, daily wear hydrogel lens wearers who were refitted with silicone hydrogel lenses reported approximately half the frequency of during-the-day and end-of-day dryness.
The study authors note that the frequency and severity of dryness symptom reports among subjects who were switched to silicone hydrogel lenses were similar to those of non-contact-lens-wearers in the cross-sectional study.5396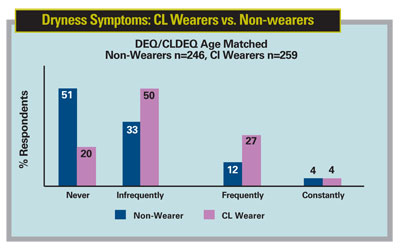
The Infection Controversy
Recent regional episodes of Fusarium-related mycokeratitis, associated with Bausch & Lomb's ReNu with MoistureLoc multipurpose contact lens care solution (now taken off the market), have been attributed to partial product evaporation, leading to a decline in the product's ability to eliminate Fusarium solani. In light of this, members of the research and development department at AMO conducted a study of several other marketed multipurpose solutions to see how evaporation affected their efficacy. The researchers used a stream of air to evaporate the MPS product to a 4X concentration. Portions were then diluted to 2X and 1X (i.e., the original concentration) for comparison. Each was tested for antimicrobial activity following Food and Drug Administration/ISO guidelines.
Results included:
• ReNu with MoistureLoc showed total loss of activity against Fusarium solani and Candida albicans, even at 2X concentration.
• Opti-Free and Opti-One brand products showed substantial reduction in activity toward S. marcescens, S. aureus and/or C. albicans.
• Polyhexamethylene biguanide hydrochloride (PHMB)-based products were found to be highly resistant to partial evaporation effects.
Of the products tested, none lost efficacy at the level of ReNu with MoistureLoc, but there were clear differences in performance between products.5367
A related study conducted at Alcon Research Ltd. evaluated how storing lenses in multipurpose solutions affected antimicrobial activity. In this study, Acuvue 2 traditional soft lenses (made of etafilcon A) were stored in side-by-side screw cap lens cases in
3 ml of solution. Solutions tested included Opti-Free Express and Opti-Free Replenish (Alcon), which contain Polyquad biocide; ReNu with MoistureLoc (previously marketed by B&L) which contains Alexidine; and Aquify (CIBA), Complete Moisture Plus (AMO), and ReNu MultiPlus (B&L), all of which contain PHMB. The lenses were stored in the manufacturer's lens cases for two, four, six, 24 and/or 48 hours, and seven days.
After storage, the lenses were removed and the solutions were tested for antimicrobial activity. Then the "spent" solutions were inoculated with Fusarium solani and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and sampled for survivors after four hours of disinfection time.
The study found that all solutions were still bactericidal after 24 hours, but two products using Alexidine and PHMB showed markedly decreased bactericidal activity after seven days of lens storage; reduced fungicidal activity was observed in as little as two hours. Also, the level of biocides remaining in these spent solutions decreased with longer storage times. However, the solutions containing Polyquad were not significantly affected by lens storage; they maintained their activity against the test microbes, and the levels of biocide in solution remained stable.5398
Higher-Order Aberrations
A Bausch & Lomb-sponsored masked, randomized, cross-over study evaluated how higher-order aberrations are affected by different brands of spherical and toric contact lenses. Thirty eyes of 15 subjects were fitted with both spherical and toric lenses in random order; brands studied were Acuvue Advance (Johnson & Johnson), Biomedics (Ocular Sciences), Frequency (CooperVision), and SofLens (B&L).
Higher-order aberrations were measured using the Zywave II Aberrometer over a 6-mm aperture, to the fifth order. Photopic and mesopic high- and low-contrast best-corrected visual acuity was measured with a 6-mm aperture.
Findings included:
• Spherical and toric lenses showed no clinically significant difference in their effect on total HOAs.
• Compared to wearing no lens, all spherical and toric lenses reduced positive spherical aberration by amounts ranging from 0.07 to 0.23 µm (p<0.0001). Frequency 55 Toric produced the greatest change in SA.
• Several significant differences were noted in vertical coma: Toric Acuvue Advance was associated with significantly less than the three prism-ballast design toric lenses; SofLens Toric had the greatest amount of vertical coma; and with the exception of Acuvue Advance, all toric lenses had significantly more vertical coma than their spherical counterparts.
• Photopic, high-contrast BCVA was better with toric Biomedics and SofLens than with Acuvue Advance (p=0.01). Photopic, low-contrast BCVA was better with toric SofLens than Acuvue Advance (p=0.03).
No other significant HOA differences were measured.5372
A team of researchers in
Data showed that in general, recently designed contact lenses reduced spherical aberration better than older designs. However, third-order aberrations increased when the lenses were off-axis by 10 degrees. In contrast, the researchers' new design showed a five-fold smaller increase in HOAs when off-center, mainly due to a much smaller increase in third-order aberrations.
The researchers do note that their new lens design is associated with an increase in spherical aberration (to 0.08 µm) when the lens is on-axis, but that this level of spherical aberration is similar to that reported in normal human eyes (0.1 µm).5374
Complications of Lens Wear
A two-year prospective case-control study conducted at the Moorfields Eye Hospital Accident and Emergency (A&E) department in London attempted to determine whether different contemporary contact lens modalities were associated with greater or lesser risk of acute, non-ulcerative complications. Case subjects were 877 new patients with contact lens-related disorders other than microbial keratitis. Two groups were used as controls: 1,069 new patient CL wearers who came in to the A&E for reasons not related to CL wear, and 639 CL wearers randomly selected from the A&E catchment area. Hospital patients completed a questionnaire; others were interviewed by telephone. Those with a medical indication for CL wear were excluded.
Findings include:
• Daily disposable CLs significantly reduced the risk of toxic and hypersensitivity disorders, compared to planned-replacement soft hydrogel lenses, but had twice the risk of mechanical disorders, and patients tended to have lens-removal difficulties.
• Silicone hydrogels were free from hypoxic complications and not significantly different from planned replacement soft hydrogels in risk of sterile keratitis, papillary conjunctivitis or acute red eye, despite a greater average frequency of overnight wear.
• Silicone hydrogels displayed a significantly greater risk of mechanical disorders than planned replacement soft hydrogels (p=0.029).
• The risk of any non-ulcerative complication was similar between CL types used for daily wear, but extended wear of any soft lens increased the risk by two to four times.5373
Researchers at the Baylor College of Medicine in

Image galleries of a typical x-y-confocal scan along the vertical axis in 1-µm z-steps after seven days of incubation in fluorescently labeled Bovine serum albumin. (Brighter green indicates a higher BSA concentration.) BSA was deposited only on the surface of the lotrafilcon B lens (left); it was deposited in higher amounts on the lens surface of a senofilcon A lens (center), with some penetrating deeper into the material. BSA is on the surface and inside the lens matrix of the etafilcon A lens (right).
The researchers investigated potential factors responsible for acquired ptosis, with special attention paid to history and duration of soft contact lens wear. In these 37 patients, soft contact lens use was the only identifiable cause of the acquired ptosis in 10 patients (27 percent). The second most common cause was found to be myasthenia gravis, in six patients (16 percent). The researchers conclude that soft contact lens wear appears to be an important cause of acquired ptosis in young patients, and that mechanisms of development are likely similar to hard contact lens use, including regular manipulation of the upper eyelid during daily contact lens insertion and removal, resulting in levator disinsertion.5389
Environmental Interaction
In a Japanese study sponsored by Johnson & Johnson, researchers sought to determine the acute effects of passive cigarette smoke exposure on the ocular surface and tear stability of contact lens wearers. Subjects were divided into two groups: The contact lens group consisted of six soft contact lens wearers and one hard contact lens wearer; the control group consisted of 10 non-contact lens wearers.
All subjects were exposed to passive smoke in a chamber where the CO concentration was maintained at 25 million ppm for five minutes. They underwent tear breakup time measurement and staining with rose bengal and fluorescein before smoke exposure and again one hour afterward. Tear samples obtained before and 24 hours after smoke exposure underwent flow cytometry to quantify inflammatory cytokine levels.
Findings include:
• One hour after exposure, TBUT was significantly reduced and fluorescein and rose bengal staining scores significantly increased in both groups.
• Following smoke exposure, IL-6 cytokine levels increased in both groups; the increase was statistically significant in the control group.
• At baseline and one hour after exposure the TBUT value was significantly lower in the contact lens group, while both staining scores and IL-6 levels were significantly higher.5409
Researchers at the University of Waterloo in Ontario used confocal microscopy to investigate how albumin penetrates into five different contact lens materials over time: omafilcon A and etafilcon A (conventional pHEMA-based materials), and balafilcon A, lotrafilcon B and senofilcon A (silicone hydrogel materials). The lenses were incubated in a protein solution consisting of bovine serum albumin, labeled with fluorescein hydrochloride, at 37 degrees Celsius.
Each material had a different absorption profile. Balafilcon A and senofilcon A showed significant albumin absorption and penetration after one day; omafilcon A absorbed significantly more albumin than etafilcon A. Overall, lotrafilcon B had the lowest albumin uptake on the lens surface and inside the matrix of all five materials, at all time points.
Dr. Asbell is a professor of ophthalmology and the director of the Cornea and Refractive Surgery Service at Mount Sinai School of Medicine in